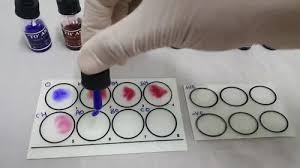
The Widal Test is a serological diagnostic method used to detect antibodies against Salmonella typhi, aiding in the diagnosis of typhoid fever. In the realm of infectious diseases, typhoid fever stands as a formidable adversary, characterized by its insidious onset and potentially severe complications if left untreated. Amidst the arsenal of diagnostic tools available, the Widal test emerges as a crucial player, providing invaluable insights into the presence of Salmonella typhi, the causative agent behind this ailment. Let’s delve into the intricacies of this diagnostic procedure, understanding its significance in the diagnosis and management of typhoid fever.
Contents
Understanding Typhoid Fever:
Before delving into the specifics of the Widal test, it’s imperative to grasp the nature of typhoid fever itself. This infectious disease primarily spreads through contaminated food and water, leading to systemic manifestations such as sustained fever, abdominal discomfort, headache, and generalized weakness. Without timely intervention, typhoid fever can progress to severe complications, including intestinal perforation and septicemia, posing a significant threat to public health, particularly in resource-limited settings.
The Widal Test:
Named after its inventor, Georges-Fernand Widal, the Widal test serves as a serological method for diagnosing typhoid fever. It operates on the principle of detecting antibodies produced by the immune system in response to Salmonella typhi antigens. While various variations of the test exist, the most common approach involves analyzing the agglutination of bacteria in the presence of patient serum, indicating the presence of specific antibodies against S. typhi. The Widal test is a serological assay used to detect antibodies against Salmonella typhi, aiding in the diagnosis of typhoid fever.
Interpreting the Results:
Interpretation of Widal test results requires a nuanced understanding of antibody titers and their significance in diagnosing typhoid fever. A significant rise in antibody titers (usually a fourfold increase) between acute and convalescent sera is suggestive of recent infection with S. typhi. However, interpreting single serum titers can be challenging due to the potential for cross-reactivity with other pathogens and variations in baseline titers among different populations. The Widal test is a serological diagnostic procedure used to detect antibodies against Salmonella typhi, aiding in the diagnosis of typhoid fever.
Challenges and Limitations:
Despite its widespread use, the Widal test is not without limitations. False-positive results can occur due to previous exposure to Salmonella species or other cross-reactive antigens, leading to misdiagnosis and unnecessary antibiotic use. Additionally, the test’s sensitivity and specificity can vary depending on factors such as the stage of infection, patient demographics, and the quality of laboratory procedures, highlighting the need for cautious interpretation and corroborative evidence from clinical evaluation and other diagnostic modalities.
Clinical Implications:
While the Widal test remains a valuable tool in diagnosing typhoid fever, its role has evolved in the context of advancing diagnostic technologies. Molecular methods such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and blood culture techniques offer higher sensitivity and specificity, enabling more accurate and timely detection of S. typhi. However, in resource-limited settings where these methods may be inaccessible, the Widal test retains its relevance as a cost-effective and relatively simple diagnostic tool, particularly in endemic regions where typhoid fever remains a significant public health concern.
Conclusion:
In the intricate tapestry of infectious diseases, the Widal test stands as a time-honored tool in the diagnosis of typhoid fever, offering valuable insights into the body’s immune response to Salmonella typhi infection. While its limitations are acknowledged, its widespread availability and cost-effectiveness make it a valuable asset, particularly in resource-limited settings. As we navigate the evolving landscape of diagnostic medicine, the significance of the Widal test serves as a reminder of the enduring quest to combat infectious diseases and safeguard public health.